A 65 year male known Hypertension ,diabetic, controlled on diet was found collapsed in bath room. On exa: Drowsy, heart rate 50 bpm with BP 140/90 and Tem 36.8 C. Jvp not raised. Heart sound normal and chest clear. Abdomen normal. Left lower limb was externally rottated and painful to move and brusing to thigh.
Lab: Hb 9.8, tlc 14000, plat 350000,
Na 135, K 6.8, urea 16, creatinine 6.7 mg/dl. Hco3 15.
t bili 1.4, AST 26, Alp 109 , Alb 4.0,
Urine : blood 2 plus, prot 1 plus,
chest xray normal , xray hip show fracture and dislocation of neck of femure.
ECg : minor t wave abnormalties in lateral leads.
Question: What is diagnosis?
What is the cause of metabolic abnormality and how will u manage the patient?
Answere: Diagnosis is Rhabdomyolysis. There are two important clues. One is that patient had a fall. Second there is renal failure with disproportionally raised creatine. There is muscle injury ( myositis). Myoglobin is released which is toxic to renal tubules and precipitate renal failure. calcium is found decrease and it binds with myoglobin and potassium and phosphate are high and there are liberated heavilly from damaged muscles.
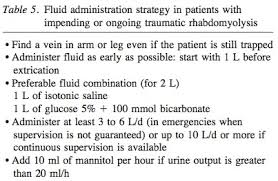
The management involves adequate hydaration and alkalinization of the urine to reduce precipitation of myoglobin in the renal tubules. Avoid loop diuretic as they cause acidic urine.

Lab: Hb 9.8, tlc 14000, plat 350000,
Na 135, K 6.8, urea 16, creatinine 6.7 mg/dl. Hco3 15.
t bili 1.4, AST 26, Alp 109 , Alb 4.0,
Urine : blood 2 plus, prot 1 plus,
chest xray normal , xray hip show fracture and dislocation of neck of femure.
ECg : minor t wave abnormalties in lateral leads.
Question: What is diagnosis?
What is the cause of metabolic abnormality and how will u manage the patient?
Answere: Diagnosis is Rhabdomyolysis. There are two important clues. One is that patient had a fall. Second there is renal failure with disproportionally raised creatine. There is muscle injury ( myositis). Myoglobin is released which is toxic to renal tubules and precipitate renal failure. calcium is found decrease and it binds with myoglobin and potassium and phosphate are high and there are liberated heavilly from damaged muscles.
The management involves adequate hydaration and alkalinization of the urine to reduce precipitation of myoglobin in the renal tubules. Avoid loop diuretic as they cause acidic urine.